This cancer begins in the pigment-producing cells found in the epidermis of the vulva.
Signs and symptoms of vulvar cancer may include:
Generally speaking, physicians know that cancer begins when a mobile develops mutations in its DNA. The mutations allow the cell to grow and divide rapidly. The cell and its own offspring go on living if other ordinary cells would die. The amassing cells form a tumor which could be cancerous, invading neighboring cells and spreading to other areas of the human body.Prevention Symptoms
Itching that does not go off soreness and tenderness Bleeding which isn't from menstruation Skin changes, such as color changes or thickening A lump, wartlike lumps or an open sore (ulcer)
Ask your doctor how often you must undergo rectal exams. These exams allow your doctor to examine your vulva and manually examine your inner organs to test for abnormalities.
Overview Vulvar cancer
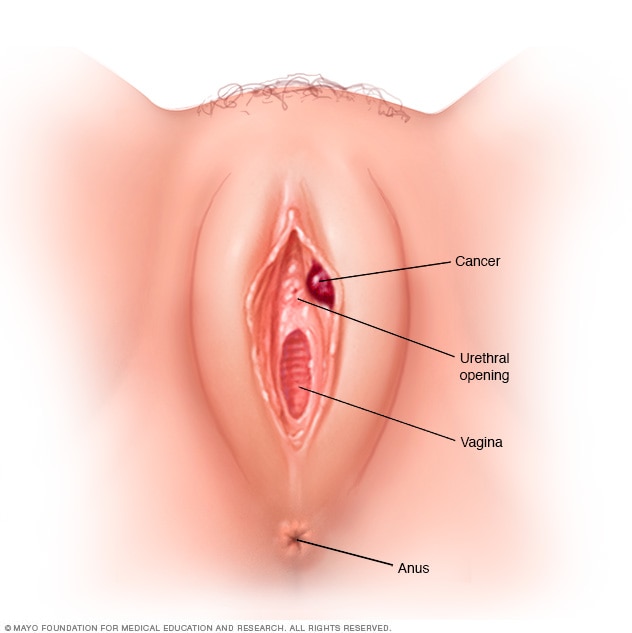 |
| Vulvar Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic |
Vulvar cancer therapy usually requires surgery to remove the cancer and a small amount of surrounding healthy tissue. Occasionally vulvar cancer surgery necessitates eliminating the whole vulva. The earlier vulvar cancer has been diagnosed, the less likely an extensive surgery is required for treatment.
Vulvar cancer treatment at Mayo Clinic
The more sexual partners you have, the greater your risk of exposure to HPV. Use a condom every time you have sex. Condoms may reduce your chance of contracting HPV but can't fully protect from it. Obtain the HPV vaccine. Kids and young adults might consider the HPV vaccine, which protects against the strains of this virus that are considered to trigger the many cases of vulvar cancer. Ask your doctor about pelvic exams
Even Though the Specific cause of vulvar cancer is not known, certain factors Seem to increase your risk of the disorder, including:
Vulvar cancer is a type of cancer which occurs on the outside surface region of the female genitalia.
Types of vulvar cancer
Speak to your physician about your risk factors for vulvar cancer along with other cervical cancers in order to ascertain the most appropriate screening exam program for you.
Vulvar cancer Symptom And Cause
CausesVulvar cancer normally forms as a lump or sore to the vulva which often causes itching. Although it can occur at any age, vulvar cancer is most frequently diagnosed in elderly adults.
The kind of cell in which vulvar cancer starts helps your doctor plan the very best treatment. The most Frequent types of vulvar cancer include:
It is not clear what triggers vulvar cancer.
Increasing age. The probability of vulvar cancer increases with age, though it can happen at any age. The average age at diagnosis is 65. Being exposed to human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a sexually transmitted disease that increases the risk of several cancers, such as vulvar cancer and cervical cancer. Most young, sexually active people are exposed to HPV, however, for most the infection goes away on its own. For many, the infection causes cell fluctuations and increases the risk of cancer in the future. Smoking. Smoking cigarettes raises the possibility of vulvar cancer. Having a weakened immune system. People who take medications to suppress the immune system, such as individuals who have undergone organ transplant, and those with illnesses that weaken the immune system, for example human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), have a higher chance of vulvar cancer. With a history of precancerous conditions of the vulva. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia is a precancerous condition that raises the risk of vulvar cancer. Most cases of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia will never develop into cancer, however, a few do opt to develop into invasive vulvar cancer. For this reason, your doctor might recommend treatment to eliminate the area of abnormal cells along with periodic follow-up checks. With a skin condition between the vulva. Lichen sclerosus, which causes the vulvar skin to become thin and itchy, increases the possibility of vulvar cancer.
To Lower Your risk of vulvar cancer, reduce your risk of the sexually transmitted disease HPV: